Understanding Empty Sac Pregnancy: A Guide for Expectant Mothers
Discovering you're pregnant is usually a joyous occasion, filled with excitement and anticipation. However, sometimes early pregnancy scans reveal a complication known as an empty sac pregnancy, also called an anechoic gestational sac. This can be a devastating and confusing experience, leaving expectant mothers with many questions and concerns. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of empty sac pregnancies, offering support and guidance to those facing this challenge.
What is an Empty Sac Pregnancy?
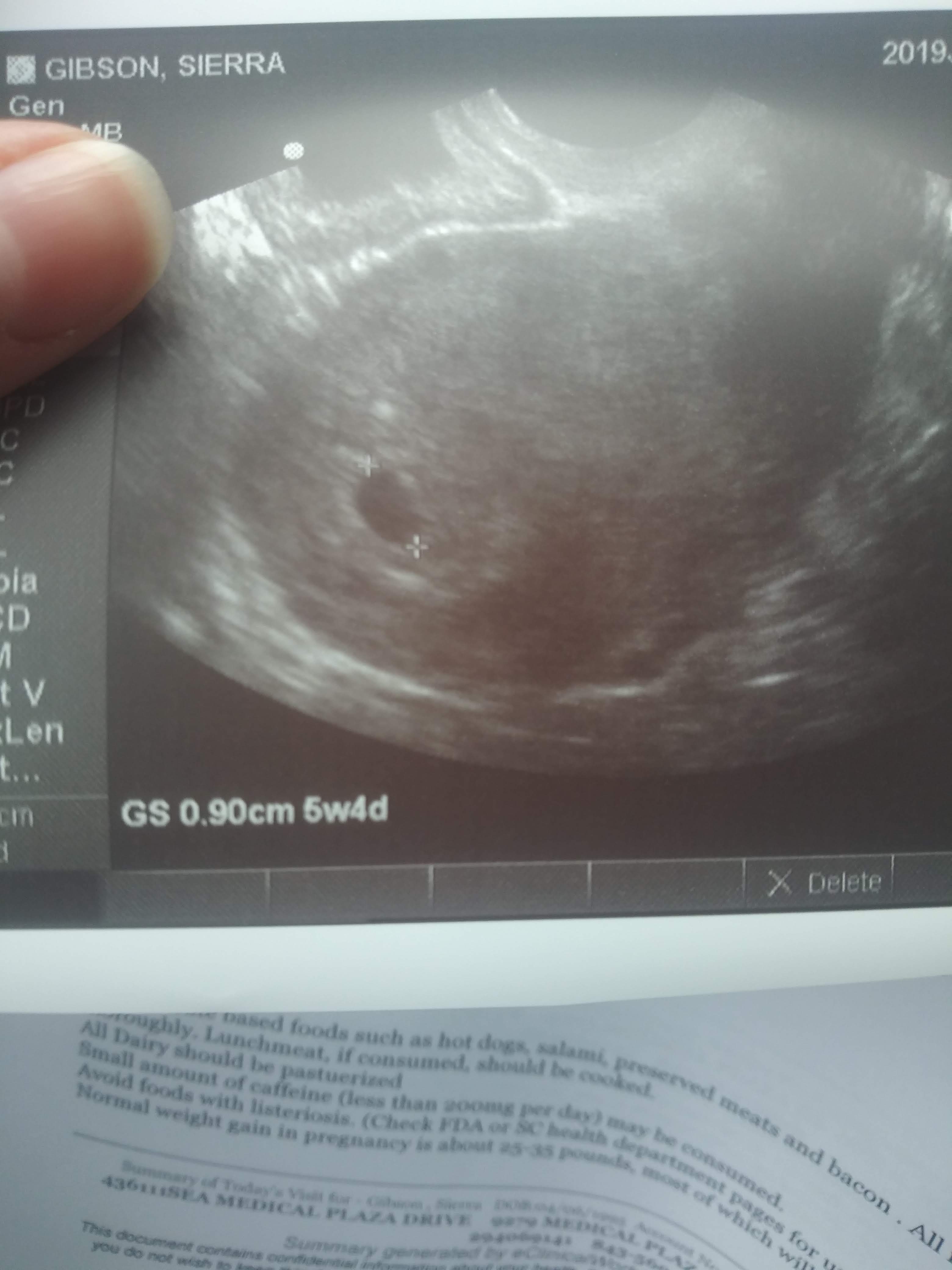
An empty sac pregnancy occurs when a gestational sac – the fluid-filled sac that develops in the uterus during early pregnancy – is seen on ultrasound, but no fetal pole (the early embryo) or fetal heartbeat is detected. This means the pregnancy hasn't progressed as expected. It's crucial to understand that this isn't the same as a miscarriage; it's a specific type of early pregnancy loss.
Key Characteristics of an Empty Sac Pregnancy:
- Presence of a gestational sac on ultrasound.
- Absence of a fetal pole (embryo).
- Absence of a fetal heartbeat.
- Usually diagnosed between 6 and 8 weeks of gestation.
Causes of Empty Sac Pregnancy:
The exact cause of an empty sac pregnancy isn't always clear, but several factors may contribute:
- Chromosomal abnormalities: The most common cause is a chromosomal abnormality in the developing embryo, making it unable to survive.
- Implantation issues: Problems with the implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterine wall can hinder development.
- Inaccurate dating of pregnancy: Sometimes, the pregnancy may be further along than initially estimated, and a fetal pole might be visible with a later scan. This is why accurate dating is crucial.
- Hormonal imbalances: Fluctuations in hormone levels can affect the development of the pregnancy.
Diagnosing an Empty Sac Pregnancy:
An empty sac pregnancy is typically diagnosed through a transvaginal ultrasound, a type of ultrasound that uses a probe inserted into the vagina for a clearer image. Your doctor may order additional tests, including blood tests to measure hormone levels (hCG).
What Happens Next?
After receiving this diagnosis, many women experience a range of emotions, from grief and sadness to confusion and anger. It's crucial to allow yourself time to process these feelings. Your doctor will discuss your options, which might include:
- Expectant management: Allowing the pregnancy to end naturally.
- Medical management: Using medication to induce miscarriage.
- Surgical management: A minor surgical procedure (dilation and curettage or D&C) to remove the pregnancy tissue.
The best course of action will depend on your individual circumstances, preferences, and medical history. Your doctor will help you make an informed decision.
Emotional Support and Recovery:
Experiencing an empty sac pregnancy is a significant loss, and it's important to seek emotional support during this difficult time. Consider talking to:
- Your partner or loved ones: Sharing your feelings with those close to you can provide comfort and support.
- Your doctor or healthcare provider: They can offer medical guidance and emotional support.
- Support groups: Connecting with other women who have experienced similar situations can provide a sense of community and understanding.
- A therapist or counselor: Professional counseling can help you process your emotions and navigate your grief.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you experience any of the following symptoms, especially during early pregnancy, contact your doctor immediately:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Heavy vaginal bleeding
- Signs of infection
Remember, you are not alone. An empty sac pregnancy is a difficult experience, but with support and understanding, you can navigate this challenging time and eventually heal. Take care of yourself, both physically and emotionally, and seek professional help when needed. Focusing on self-care and allowing yourself time to grieve is crucial for your well-being.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.