Troubleshooting Turbo Vane Position Sensor Issues: Reducing Drop Rates
The turbocharger, a critical component in modern diesel engines, relies on precise control to optimize performance and efficiency. A malfunctioning turbo vane position sensor can lead to significant issues, including reduced power, increased emissions, and, critically, increased drop rates. This article delves into the common problems associated with this sensor and provides practical troubleshooting steps to minimize downtime and maintain optimal engine performance.
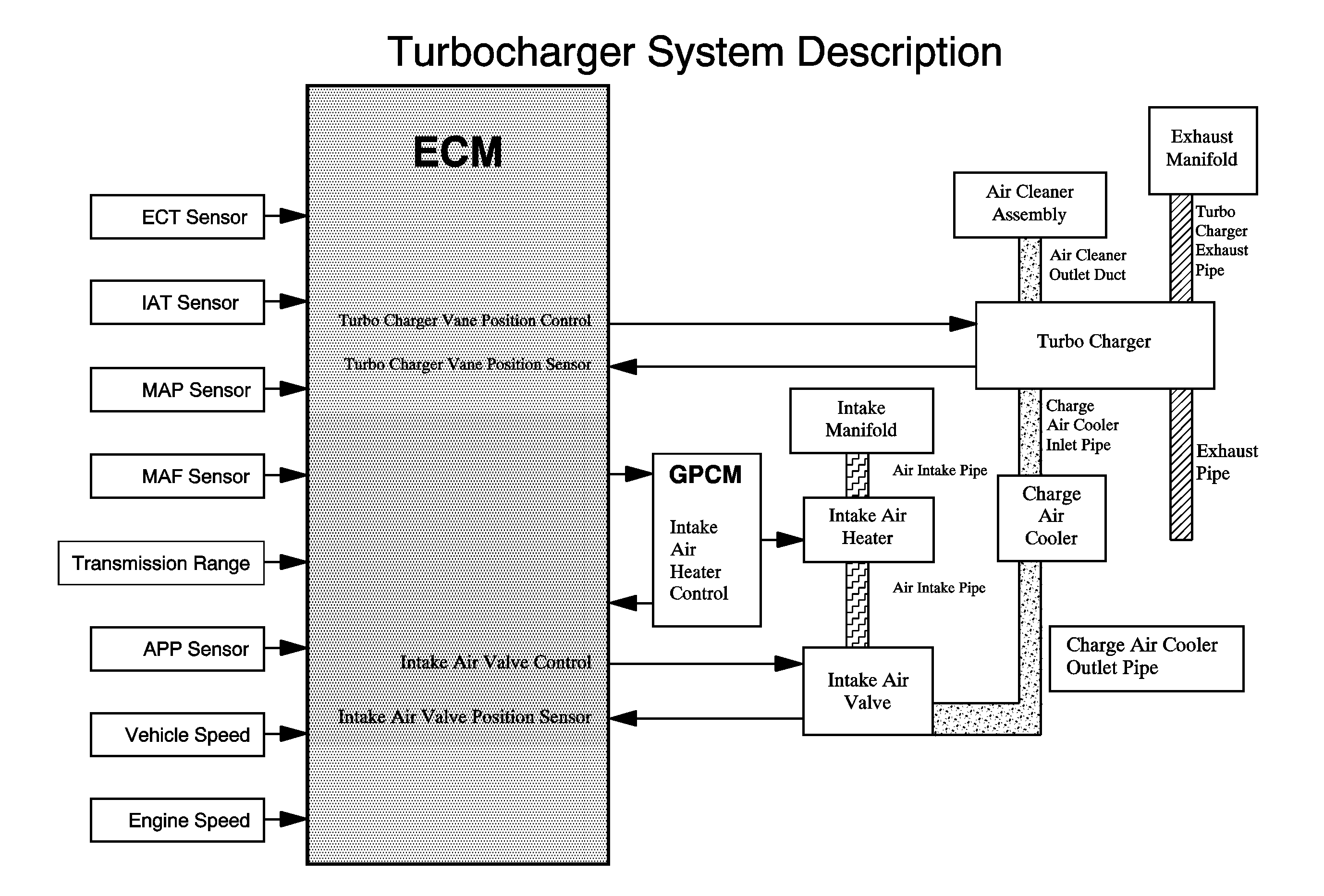
Understanding the Turbo Vane Position Sensor
The turbo vane position sensor (TVPS) plays a vital role in controlling the variable geometry turbine (VGT) within the turbocharger. This system adjusts the vanes within the turbine housing, optimizing airflow based on engine load and speed. The TVPS monitors the position of these vanes, providing feedback to the engine control unit (ECU). Accurate sensing is crucial for maintaining optimal boost pressure and efficient combustion.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty TVPS
A malfunctioning TVPS can manifest in several ways, often impacting operational efficiency and resulting in higher drop rates:
- Reduced Engine Power: The most noticeable symptom is a significant loss of engine power, especially under load. The ECU may be restricting boost pressure due to inaccurate sensor readings.
- Increased Emissions: Incorrect vane positioning can lead to incomplete combustion, resulting in higher levels of particulate matter (PM) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions. This can lead to failed emissions tests and potential penalties.
- Rough Engine Idle: A faulty TVPS can cause instability in engine idle, leading to rough running and vibrations.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): The ECU will likely illuminate a CEL, indicating a problem within the engine's control system, often accompanied by diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Increased Drop Rates: This is arguably the most significant consequence, leading to costly downtime and reduced productivity. Inaccurate boost control directly impacts the engine's ability to consistently operate within its optimal parameters.
Troubleshooting Steps
Diagnosing TVPS issues requires a systematic approach:
-
Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use a diagnostic scanner to retrieve any stored DTCs related to the turbocharger or boost pressure control. These codes provide valuable clues to the problem's location.
-
Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Carefully examine the wiring harness and connectors leading to the TVPS for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Repair or replace damaged components as needed.
-
Visual Inspection of the TVPS: Check the sensor itself for any physical damage or signs of wear. A damaged sensor needs replacing.
-
Sensor Voltage and Resistance Check: Use a multimeter to check the sensor's voltage and resistance readings against the manufacturer's specifications. Deviations from the specified values often indicate a faulty sensor.
-
Actuator Test: Test the VGT actuator to ensure it's responding correctly to commands from the ECU. A malfunctioning actuator can mimic the symptoms of a faulty TVPS.
-
Boost Pressure Measurement: Measure the actual boost pressure using a pressure gauge and compare it to the expected values based on engine load and speed. Discrepancies indicate a problem within the boost control system.
Minimizing Drop Rates: Preventative Maintenance and Best Practices
Preventing TVPS failure contributes significantly to reducing drop rates:
- Regular Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance checks including inspections of the turbocharger system and associated components.
- Proper Engine Operation: Avoid prolonged periods of idling or operating the engine under extreme conditions.
- Clean Air Filters: Regularly replace air filters to prevent the ingestion of debris that can damage the turbocharger.
- High-Quality Lubricants: Use lubricants that meet the manufacturer's specifications to ensure optimal lubrication of the turbocharger.
Conclusion
Addressing TVPS issues promptly is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and minimizing costly downtime. By following the troubleshooting steps and adopting preventative maintenance practices, you can significantly reduce drop rates and ensure the longevity of your diesel engine. Remember to always consult your engine's service manual for specific diagnostic procedures and specifications. Ignoring these issues can lead to more extensive and costly repairs down the line.