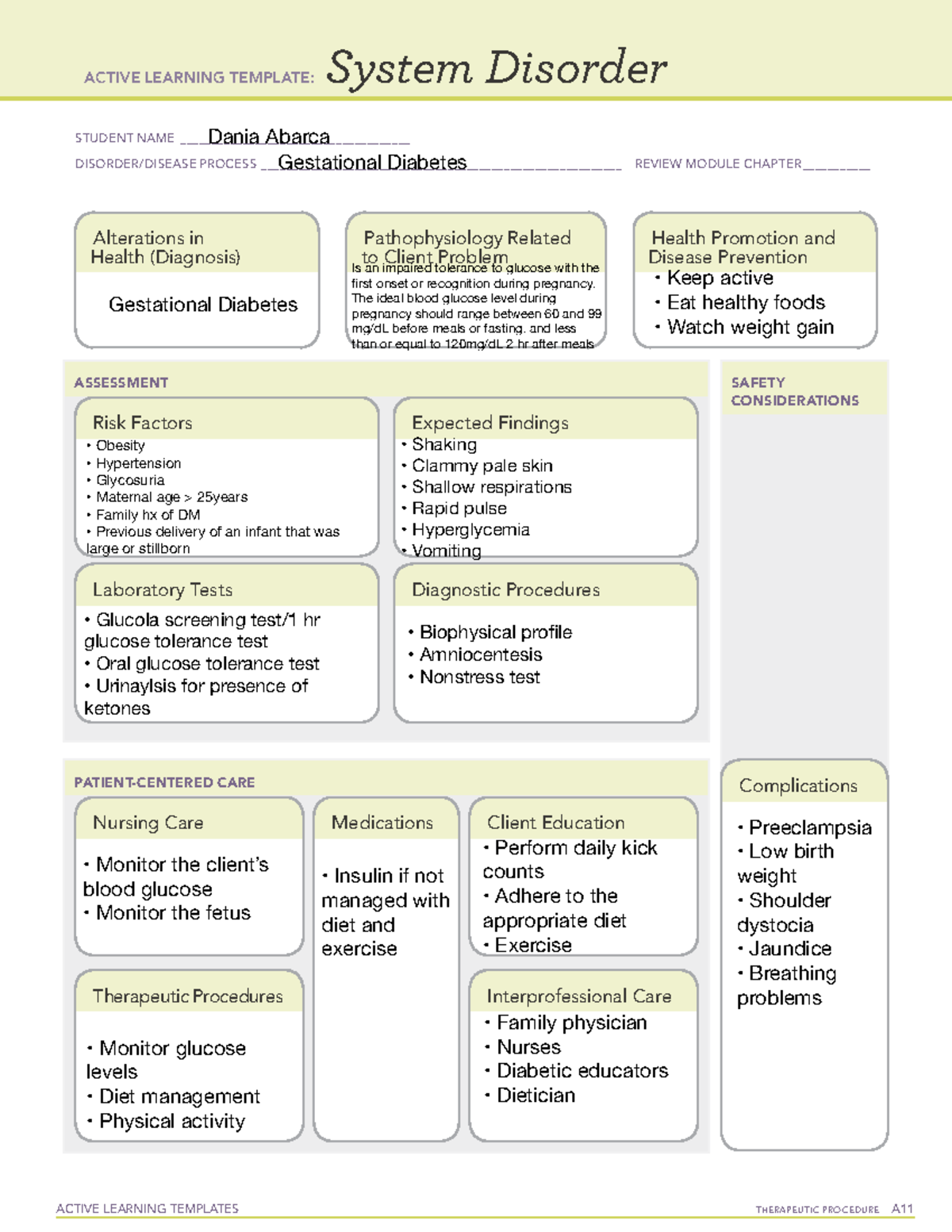
ATI Diagnostic Template for Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide for Nurses
Diabetes mellitus is a prevalent chronic condition requiring meticulous management. Nurses play a crucial role in assessing, diagnosing, and managing diabetes in their patients. Understanding and effectively utilizing diagnostic templates, like those provided by ATI (Assessment Technologies Institute), is key to providing high-quality, patient-centered care. This comprehensive guide will explore the ATI diagnostic template for diabetes, offering valuable insights for nurses at all levels of experience.
Understanding the ATI Diagnostic Template
The ATI diagnostic template for diabetes isn't a single, standalone document. Rather, it's a framework guiding nurses in systematically collecting and analyzing patient data related to diabetes. This framework helps ensure a thorough assessment encompassing various aspects of the disease, from physiological markers to psychosocial factors. Key components typically included are:
- Patient Demographics and History: Age, gender, medical history (including family history of diabetes), lifestyle factors (diet, exercise, smoking), and current medications are crucial starting points.
- Physical Assessment: This includes vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate), weight, height, and a focused assessment of the integumentary system (checking for skin lesions indicative of diabetic complications), and neurological system (assessing for neuropathy).
- Laboratory Data Interpretation: This is a cornerstone of diabetes diagnosis and management. The template guides nurses in interpreting key lab results such as:
- Fasting Blood Glucose (FBG): Used to screen for and diagnose diabetes.
- HbA1c (Glycated Hemoglobin): Measures average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Used to diagnose gestational diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance.
- Urine Analysis: Checks for the presence of glucose and ketones.
- Medication Reconciliation: A comprehensive list of current medications, including insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents, is essential to avoid drug interactions and ensure safe and effective treatment.
- Patient Education and Counseling: Documentation of patient understanding and adherence to the treatment plan is vital. The template might include sections for documenting patient education provided and the patient's understanding of self-management techniques.
- Nursing Diagnoses: Using the collected data, nurses formulate nursing diagnoses based on the patient's specific needs, such as imbalanced nutrition, risk for infection, or ineffective health maintenance.
- Planning and Interventions: This section outlines the nursing interventions aimed at addressing the identified nursing diagnoses.
- Evaluation: This final section documents the effectiveness of the interventions and any necessary adjustments to the care plan.
Utilizing the ATI Template Effectively
Mastering the ATI diagnostic template requires practice and a strong understanding of diabetes pathophysiology and management. Here are some tips for effective utilization:
- Familiarize Yourself with the Template: Thoroughly review the template structure and understand the purpose of each section.
- Systematic Data Collection: Follow a structured approach to data collection to avoid omissions.
- Accurate Data Entry: Ensure all data entered is accurate and complete.
- Critical Thinking and Analysis: Don't just record data; analyze it to identify patterns and trends.
- Collaboration: Work collaboratively with other members of the healthcare team, including physicians and dieticians.
Beyond the Template: Enhancing Diabetes Care
While the ATI diagnostic template provides a valuable framework, remember that effective diabetes management extends beyond the template itself. Continuous professional development, staying up-to-date on the latest advancements in diabetes care, and prioritizing patient education are crucial aspects of providing holistic care.
Resources for Nurses:
- American Diabetes Association (ADA):
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK):
By mastering the ATI diagnostic template for diabetes and utilizing these additional resources, nurses can significantly enhance their ability to provide high-quality, comprehensive care to patients living with diabetes. Remember that this is a continuously evolving field; ongoing learning is essential to remain proficient and provide the best possible patient outcomes.